



The freezer motor is a fundamental component in modern refrigeration appliances, playing a crucial role in maintaining optimal temperatures for food preservation. As noted by industry expert Dr. Emily Carter, a leading authority in refrigeration technology, "Understanding the functionality of the freezer motor allows consumers to appreciate the efficiency and engineering behind their appliances." This statement underscores the importance of comprehending how the freezer motor operates and its impact on energy consumption and performance.

In 2025, as technology continues to evolve, the design and efficiency of freezer motors will undoubtedly become more sophisticated, catering to the growing demand for energy-efficient and reliable appliances. By delving into the mechanics and working principles of the freezer motor, homeowners can make informed choices when it comes to appliance selection and maintenance.
As we explore the intricate workings of the freezer motor, we will uncover its various components, operation methods, and the significance of regular maintenance, all of which contribute to the longevity of your appliance and enhance its functionality in the long run.
A freezer motor is a critical component in refrigeration appliances, responsible for maintaining low temperatures necessary for food preservation. This motor powers the compressor, which compresses refrigerant gas and circulates it through the refrigeration system. As the refrigerant moves through the coils, it absorbs heat from inside the freezer, allowing the appliance to cool efficiently. The motor's operation is vital in ensuring that the freezer consistently reaches and maintains the desired temperature.
In terms of functionality, freezer motors operate based on a cycle that includes several stages, including compression, condensation, and expansion. When the thermostat detects that the internal temperature of the freezer is rising above a set level, it triggers the motor to start. This initiates the compressor, which begins to compress the refrigerant, transforming it into a high-pressure gas. As it moves into the condenser coils, the refrigerant releases heat and changes back into a liquid state, ready to absorb more heat when it returns to the evaporator coils. This continuous cycle allows the freezer motor to ensure that food remains frozen and fresh, demonstrating its integral role in modern refrigeration appliances.
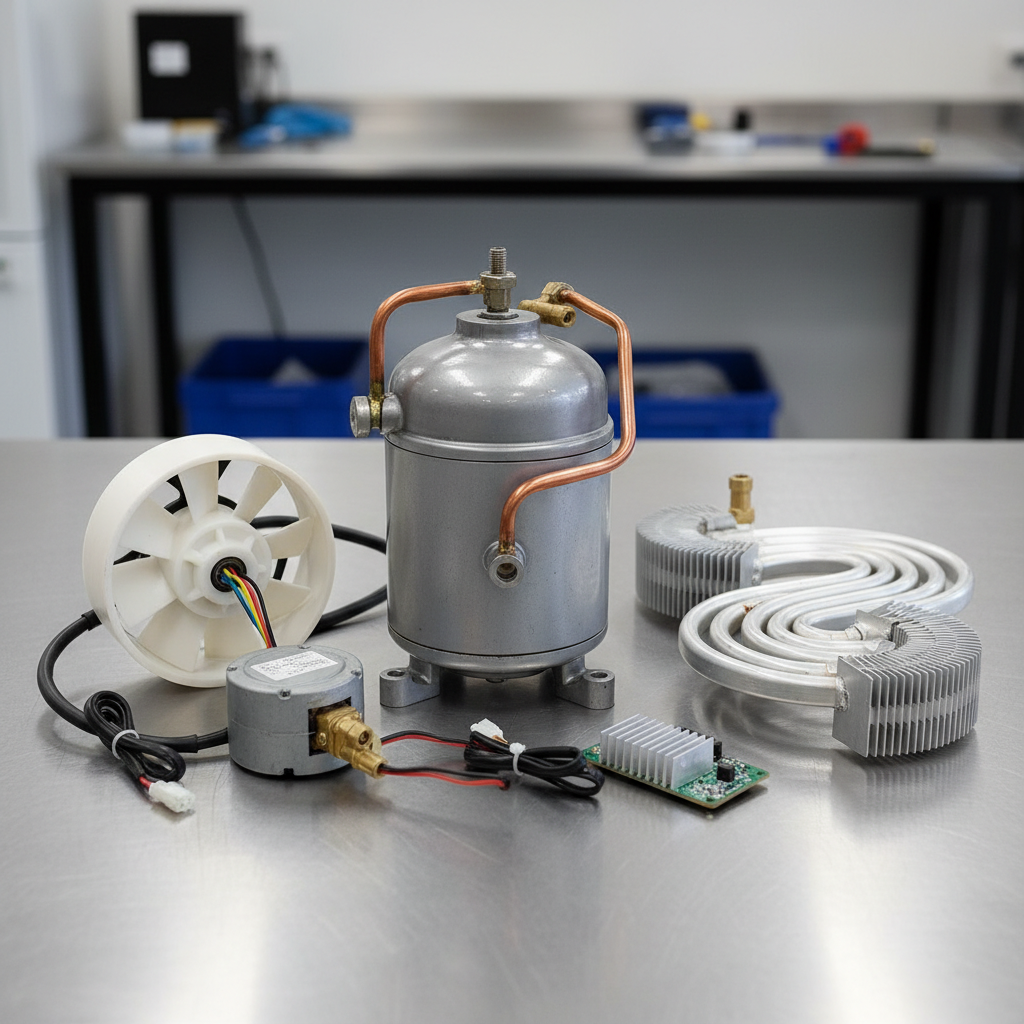

A freezer motor is a crucial component of any refrigeration appliance, playing a significant role in maintaining optimal cooling efficiency. Its key components include the compressor, fan motor, and evaporator. The compressor is often referred to as the heart of the freezer, as it circulates refrigerant through the system, compressing it to raise its temperature and pressure before sending it to the coils. This process not only helps in removing heat from inside the appliance but also facilitates the cooling cycle necessary for food preservation.
The fan motor, on the other hand, supports air circulation within the freezer. By distributing cool air evenly throughout the compartment, it prevents temperature fluctuations that can lead to spoilage. Additionally, the evaporator works in tandem with the compressor, absorbing heat from inside the unit as the refrigerant evaporates. Together, these components ensure that the freezer operates efficiently, minimizing energy consumption while maximizing its capability to keep food frozen and fresh. Understanding these key elements helps users appreciate the complexity and efficiency of their freezer appliances.
Freezer motors play a critical role in the energy consumption of refrigeration appliances. With the global refrigeration monitoring market projected to surpass USD 24.40 billion by 2034, understanding the efficiency of freezer motors is paramount. Recent analysis indicates that user behavior significantly influences energy usage, suggesting that simple changes in how appliances are used can drive down costs. For instance, optimizing operating times and maintaining appropriate temperature settings can improve the overall efficiency of a freezer motor.
Tips: Regularly clean the coils and ensure your freezer is stocked appropriately; this helps maintain efficiency and reduces the workload on the motor. Implementing advanced technologies such as performance optimization systems can lead to substantial energy savings, as evidenced by major retailers cutting energy use by 10% with innovative solutions.
According to market studies, the AI refrigerator segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 20.20%, highlighting the industry's shift towards smarter, energy-efficient appliances. As more refrigerators integrate AI for operational precision, the potential for reducing energy consumption while enhancing performance will provide both economic benefits and environmental sustainability.
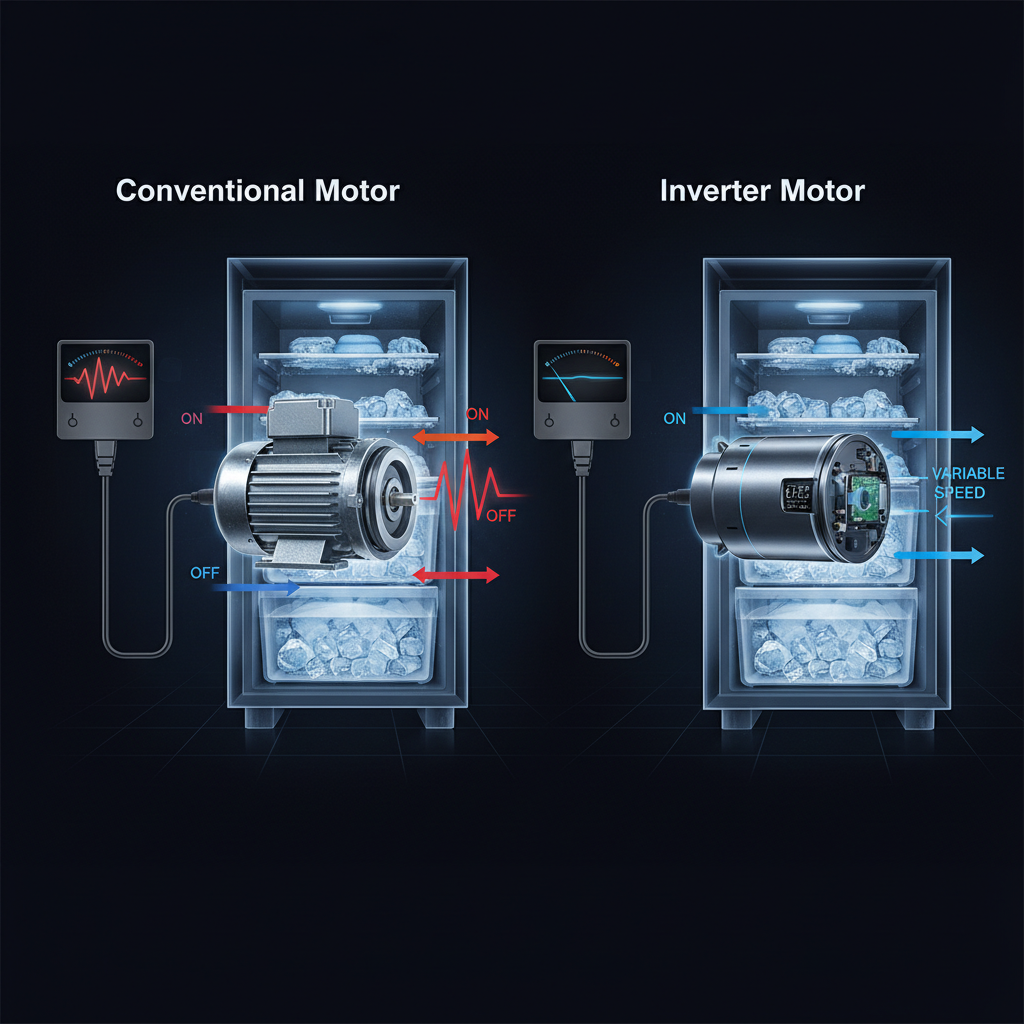
In exploring the comparative performance of conventional versus inverter freezer motors, it's essential to understand their operational differences and the implications for energy savings. Conventional freezer motors typically operate at a fixed speed, turning on and off to maintain the desired temperature. This on-off cycling can lead to energy spikes and inefficient power consumption, as the motor works hard to reach the set temperature each time it restarts. Consequently, the constant fluctuations can lead to increased wear and tear on the motor and other components.
In contrast, inverter freezer motors employ variable speed technology, allowing them to adjust their operation based on cooling demands. This means that the motor can run at lower speeds during periods when less cooling is required, such as when the freezer is not frequently opened. By maintaining a steady temperature with reduced energy consumption, inverter motors can significantly cut electricity costs over time. Additionally, their efficient performance often results in quieter operation and extended appliance lifespan, making them an appealing choice for energy-conscious consumers.
As the demand for energy-efficient appliances rises, freezer motor technology is evolving to meet new sustainability standards. According to a recent report by the International Energy Agency, energy-efficient motors can reduce electricity consumption by over 30% compared to traditional designs. This trend is pushing manufacturers to develop advanced freezer motor systems that not only lower energy usage but also extend appliance lifespan. Innovations such as brushless DC motors and inverter technology are leading the way, providing quieter operation and precise temperature control.
Tip: When choosing a freezer, look for models with Energy Star ratings, as these typically incorporate the latest motor technologies for better efficiency.
Furthermore, advancements in smart technology are reshaping freezer motor applications. Integrated sensors and networking capabilities allow for real-time performance monitoring and maintenance alerts, enhancing user convenience and energy management. Research indicates that smart appliances will dominate over 70% of the market by 2025, urging manufacturers to prioritize these features in their designs.
Tip: Investing in smart freezers can provide long-term savings through energy efficiency, as many models offer adaptive cooling systems that adjust based on usage patterns.








